Endometrial Biopsy
The uterus is lined by the special type of tissue known as Endometrium. An endometrial biopsy involves removal a 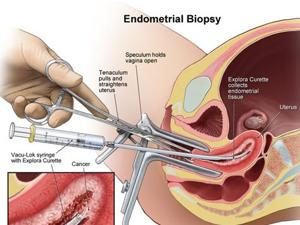 small piece of tissue from the lining of the uterus.
small piece of tissue from the lining of the uterus.
The sample of tissue is analyzed under a microscope in the laboratory by the doctors to find out the problems in the endometrium. An endometrium biopsy also helps doctors to determine the hormone levels.
An endometrial biopsy is also used to determine the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding when the patient experiences a change in her normal pattern of menstrual bleeding or when bleeding is unexpected.
Looking for a free cost estimate for treatment abroad.
It can also be done to help evaluate the cause of infertility. This test is also used to check the cancer of the uterus. An Endometrial biopsy takes 15-20 minutes.
An endometrial test should be scheduled during a certain time in your menstrual cycle. Doctor will insert a speculum into the vagina to hold it open so that your cervix can be viewed.
The Cervix is washed with a special solution. Doctors will insert a metal tool through the cervix to theuterus.
A small piece of the inner lining tissue is collected from the uterus and thetool is removed from the uterus.
Sometimes a local anesthesia is spray or injected into your cervix. The sample tissue is put into the fluid and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
The sample is examined under a microscope by the doctors. The results will come out after the 5-6 days of the test.
This test is designed to evaluate whether the lining of the uterus (endometrium) has been properly stimulated hormonally to allow a fertilized egg to implant and grow into a pregnancy.If the abnormal tissues are detected in the results, your doctor will recommend a course of medical or surgical treatment.













