Cryopreservation
Cryopreservation is the process in which the organelles, cells, tissues, extracellular, matrix, organs or the other biological constructs which are susceptible to the damage caused by the unregulated chemical kinetics are preserved by cooling at a very low temp .This preservation makes it possible to store the cells as well as other biological materials unchanged for centuries.
Do you have your medical reports, send us now for a free quote
- To help cells to survive at an extreme low cooling temperature and thawing back to the physical condition.
- Intracellular ice formation is the other critical issue and it needs to be controlled to keep the cell membrane intact and the cells alive.
- A Vital element to prevent this is the freezing rate and the composition of the freezing medium used.
- Freezing medium consists of the diluter, protein source and cryoprotectant compound.
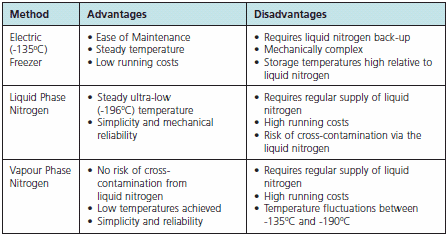
Phenomena’s which are the cause of the damage to the cells during cryopreservation are said to occur during the freezing stage which includes solutions effects, extracellular ice formation, dehydration and the intracellular ice formation.
Solution effects
As ice crystals grow in freezing water, solutes are excluded, causing them to become concentrated in the remaining liquid water. High concentrations of some solutes can be very damaging.
Extracellular ice formation
When tissues are cooled slowly, water migrates out of cells and ice forms in the extracellular space. Too much extracellular ice can cause mechanical damage to the cell membrane due to crushing.
Dehydration
Migration of water, causing extracellular ice formation, can also cause cellular dehydration. The associated stresses on the cell can cause damage directly.
Intracellular ice formation
While some tissues can tolerate some extracellular ice, any appreciable intracellular ice is almost always fatal to cells.
Cryopreservation is done for the thin samples and the small clumps of the individual cells because these can be cooled more quickly and so require lesser doses of toxic cryoprotectants. Tissue are widely frozen under cryopreservation .
Embryo cryopreservation
Cryopreservation for embryos are used for embryo storage, e.g. when in vitro fertilization has resulted in more embryos than is currently needed.
Ovarian tissue cryopreservation
Cryopreservation of ovarian tissue is of interest to women who want to preserve their reproductive function beyond the natural limit, or whose reproductive potential is threatened by cancer therapy,[28] for example in hematologic malignancies or breast cancer.
Oocyte cryopreservation
Human Oocyte cryopreservation is a new technology in which a woman’s eggs (oocytes) are extracted, frozen and stored. Later, when she is ready to become pregnant, the eggs can be thawed, fertilized, and transferred to the uterus as embryos
Semen cryopreservation
Semen is used for cryopreservation and it can be stored for 22 years long. Semen cryopreservation can be used for sperm donation when the recipients want the treatment in the different place or as means of preserving fertility for men undergoing the vasectomy.
Testicular tissue Cryopreservation
Cryopreservation of immature testicular tissue is a developing method to avail reproduction to young boys who need to have genotoxic therapy. Animal data are promising since healthy offsprings have been obtained after transplantation of frozen testicular cell suspensions or tissue pieces













